Kafka Consumer
The PDI client pulls streaming data from Kafka through a Kafka transformation. The parent Kafka consumer step runs a child (sub-transformation) that executes according to message batch size or duration, letting you process a continuous stream of records in near real-time. The child transformation must start with the Get records from stream step.
You can configure the Kafka consumer step to continuously ingest streaming data from your Kafka server or stop the consumer at a particular time. Depending on your setup, you can execute the transformation within PDI.
In the Kafka consumer step itself, you can define the number of messages to accept for processing, as well as the specific data formats to stream activity data and system metrics. You can set up this step to collect monitored events, track user consumption of data streams, and monitor alerts.
Additionally, from the Kafka consumer step, you can select a step in the child transformation to stream records back to the parent transformation. This allows records processed by a Kafka consumer step in a parent transformation to be passed downstream to any other steps included within the same parent transformation.
Kafka records are stored within topics and consist of a category to which the records are published. Topics are divided into a set of logs known as partitions. Kafka scales topic consumption by distributing partitions among a consumer group. A consumer group is a set of consumers sharing a common group identifier.
Before using the Kafka consumer step, you must configure a named connection for your distribution. For information on named connections, see Connecting to a Hadoop cluster with the PDI client.
You can stop the consumer ingestion by entering a stop date in the Offset Settings tab. You can also use SSL and SASL secure connections by providing the configuration information explained in the Options tab topic.
General
The Kafka consumer step requires definitions for setup, batch, fields, result fields, Kafka-specific options, and Offset Settings to stream messages.
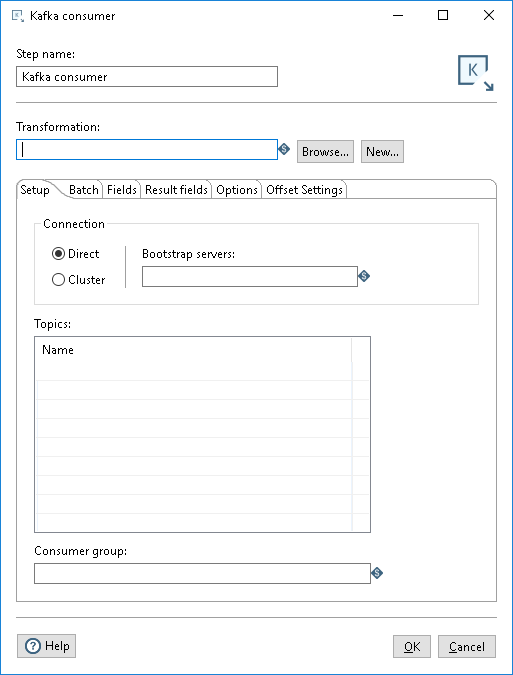
Enter the following information in the Step name and Transformation fields:
| Option | Description |
| Step name | Specifies the unique name of the step on the canvas. The Step name is set to Kafka consumer by default. |
| Transformation |
Specify the child transformation to execute by performing any of the following actions:
The selected child transformation must start with the Get Records from Stream step. If you select a transformation that has the same root path as the current transformation, the variable ${Internal.Entry.Current.Directory} is automatically inserted in place of the common root path. For example, if the current transformation's path is /home/admin/transformation.ktr and you select a transformation in the directory /home/admin/path/sub.ktr, then the path is automatically converted to ${Internal.Entry.Current.Directory}/path/sub.ktr. If you are working with a repository, you must specify the name of the transformation. If you are not working with a repository, you must specify the XML file name of the transformation. Transformations previously specified by reference are automatically converted to be specified by the transformation name in the Pentaho Repository. |
Create and save a new child transformation
Procedure
-
In the Kafka consumer step, click New. The Save As dialog box appears.
-
Navigate to the location where you want to save your new child transformation, then type in the file name.
-
Click Save. A notification box displays informing you that the child transformation has been created and opened in a new tab. If you do not want to see this notification in the future, select the Don't show me this again check box.
-
Click the new transformation tab to view and edit the child transformation. It automatically contains the Get Records from Stream step. Optionally, you can continue to build this transformation and save it.
-
When finished, return to the Kafka consumer step.
Options
The Kafka consumer step features several tabs. Each tab is described below.
Setup tab
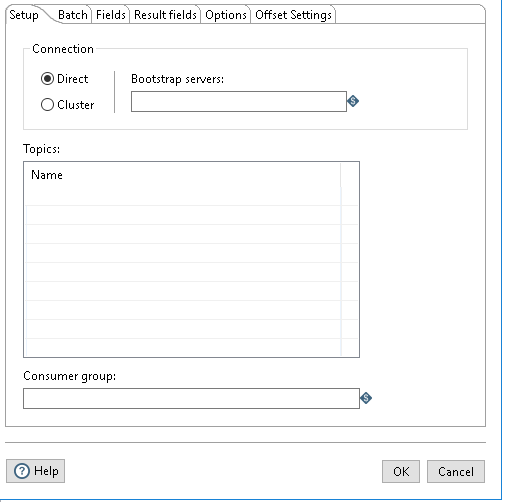
In this tab, define the connections used for receiving messages, topics to which you want to subscribe, and the consumer group for the topics.
| Option | Description |
| Connection |
Select a connection type:
|
| Topics | Enter the name of each Kafka topic from which you want to consume streaming data (messages). You must include all topics that you want to consume. |
| Consumer group |
Enter the name of the group of which you want this consumer to be a member. Each Kafka consumer step starts a single thread for consuming. When part of a consumer group, each consumer is assigned a subset of the partitions from topics it has subscribed to, which locks those partitions. Each instance of a Kafka consumer step will only run a single consumer thread. |
Batch tab
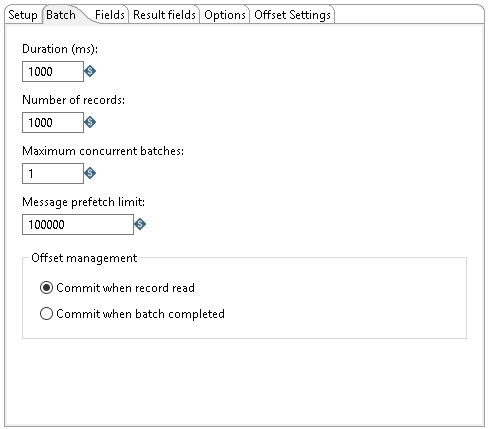
Use this tab to designate how many messages to consume before processing. You can specify message count and/or a specific amount of time.
The number of messages consumed before processing is defined by either the Duration (ms) or the Number of records option. Messages are consumed when either the specified duration or number of records occur. For example, if Duration (ms) is set to 1000 milliseconds and Number of records is 1000, messages are consumed for processing whenever time intervals of 1000 milliseconds are reached, or 1000 records have been received. If you set either option to zero, PDI will ignore that parameter.
You can also specify the maximum number of batches used to collect records at the same time.
| Option | Description |
| Duration (ms) | Specify a time in milliseconds. This value is the amount of time the step will spend collecting records prior to the execution of the transformation.
If this option set to a value of 0, then Number of records triggers consumption. Either the Duration or the Number of records option must contain a value greater than 0 to run the transformation. |
| Number of records | Specify a number. After every ‘X’ number of records, the specified transformation will be executed, and these ‘X’ records will be passed to the transformation.
If this option is set to a value of 0 then Duration triggers consumption. Either the Duration or the Number of records option must contain a value greater than 0 to run the transformation. |
| Maximum concurrent batches | Specify the maximum number of batches used to collect records at the same time. The default value is 1, which indicates a single batch is used for collecting records.
This option should only be used when your consumer step cannot keep pace with the speed at which the data is streaming. Your computing environment must have adequate CPU and memory for this implementation. An error will occur if your environment cannot handle the maximum number of concurrent batches specified. |
| Message prefetch limit | Specify a limit for how many incoming messages this step will queue for processing, as they are received from the broker. Setting this value forces the broker to manage the backpressure of messages exceeding the specified limit. The default number of messages to queue is 100000. |
| Offset management | Select one of the two following options to manage the offset:
|
Fields tab
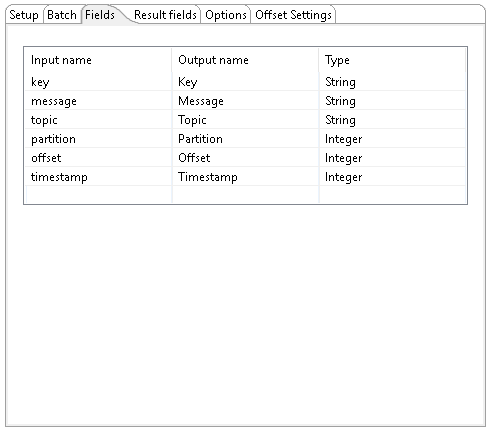
Use this tab to define the fields in the record format.
| Option | Description |
| Input name |
The input name is received from the Kafka streams. The following are received by default:
|
| Output name | The Output name can be mapped to subscriber and member requirements. |
| Type |
The Type field defines the data format for streaming the record. You must choose the same data type that produced the records. This field applies to the key and message input names. Options include:
|
Result fields tab
Use this tab to select the step from the child transformation, which will stream records back to the parent transformation. This allows records processed by a Kafka consumer step in the parent transformation to be passed downstream to any other steps included within the same parent transformation.
- Return fields from: Select the name of the step (from the child transformation) that will stream fields back to the parent transformation. The data values in these returned fields will be available to any subsequent downstream steps in the parent transformation.
Options tab
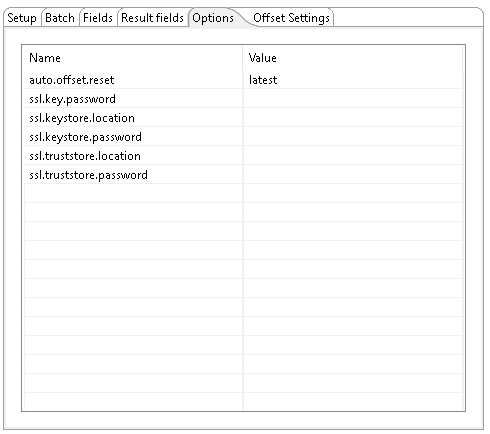
Use this tab to send the options to broker while connecting from consumers. The option values can be encrypted. A few of the most common options are included for your convenience. You can enter any desired Kafka property. For further information on these input names, see the Apache Kafka documentation site: https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/.
Offset Settings tab
Use this tab to stop the Kafka consumer when the messaged offset timestamp reaches the input timestamp in this screen. By using this tab and the Kafka offset job, you can read messages from the start offset timestamp to the end offset timestamp. Kafka consumer runs in normal mode if no input is provided on this tab.
| Option | Description |
| Offset timestamp | Specifies the end timestamp to stop the consumer when the message offset timestamp reaches the input timestamp |
| Timestamp format |
Specifies the timestamps format for the offset. When an epoch value is given, the timestamp format is not needed. |
Modes
You can run the Kafka consumer step in three different modes using the Offset Settings tab.
- Infinite loop
- End Timestamp to stop consumer
- Read data between two-time stamps
If you do not enter a value in the Offset timestamp field, the Kafka consumer runs in an infinite loop by default.
When you enter a value in Offset timestamp field, it is considered as the end time and the consumer stops when it reaches that time.
By using the Kafka consumer step in conjunction with the Kafka Offset job, you can consume data between a start time and an end time, using either secure or non-secure connections. The Offset timestamp value in the Kafka Offset job is considered the start time and the Offset timestamp value in the Kafka Consumer step is considered the end time.
For example, if you set the Offset timestamp value in the Kafka Offset job to 23/08/02 07:03:00 and set the Offset timestamp value in the Kafka consumer step to 23/08/04 07:03:00, you will consume the data for a 48 hour period.
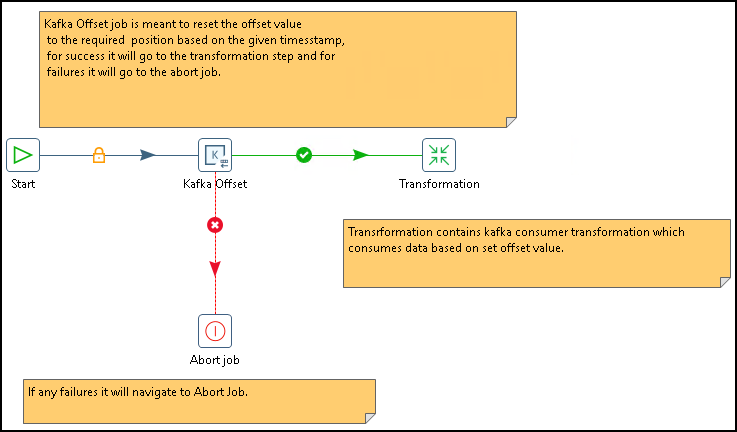
This kafka_job.kjb sample shown below is located in the design-tools/data-integration/plugins/pentaho-streaming-kafka-plugin-zip-9.5.1.0-110/pentaho-streaming-kafka-plugin/samples/transformations directory and demonstrates using the Kafka Offset job with the Kafka consumer step
Security
You can implement security for the Pentaho Kafka consumer step using either an SSL, SASL or SASL SSL connection.
Using SSL
Procedure
-
On the Setup tab, select the Direct connection and enter ${KAFKA_ssl_url} as the Bootstrap servers URL.
-
On the Options tab, enter the options and values listed in the following table:
Option Value auto.offset.resetlatestssl.key.password$[Key password]ssl.keystore.location$[Path to Key store]ssl.keystore.password$[Key store password]ssl.truststore.location$[Path to Trust store]ssl.truststore.password$[Trust store Password]ssl.protocolTLS 1.2security.protocolSSL -
Click OK.
Using SASL
SASL security requires the Kerberos configuration file krb5.conf and a Kerberos principal. You must obtain these from your Kerberos administrator.
Perform the following steps to set up SASL security for PDI to connect to the Kafka broker:
Procedure
-
Copy the krb5.conf file to the ${JAVA_HOME}/conf/security directory.
-
Run the kinit command
${KERBEROS_PRINCIPAL_KAFKA}to initiate the authentication process to obtain a Kerberos ticket-granting ticket (TGT). -
Copy the ${KERBEROS_PRINCIPAL_KAFKA}.keytab from the server to the workstation where PDI is installed.
-
On the Setup tab, select the Direct connection and enter ${KAFKA_SASL_PLAINTEXT_URL} as the Bootstrap servers URL.
-
On the Options tab, enter the options and values listed in the following table:
Option Value auto.offset.resetlatestsecurity.protocolSASL_PLAINTEXTsasl.mechanismGSSAPIsasl.kerberos.service.name${KERBEROS_KAFKA_SERVICE_NAME}sasl.jaas.config${SASL_JAAS_CONFIG} -
Click OK.
Next steps
${SASL_JAAS_CONFIG}
com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required useKeyTab=true storeKey=true debug=true doNotPrompt=true keyTab="Path to ${KERBEROS_PRINCIPAL_KAFKA}.keytab" principal="${Pricipal created in Kerberos for Kafka}";
Using SASL SSL
Perform the following steps to set up SASL SSL security for PDI to connect to the Kafka broker:
Procedure
-
On the Setup tab, select the Direct connection and use ${KAFKA_KERBEROS_SSL_URL} as the URL.
-
On the Options tab, enter the options and values listed in the following table:
Option Value auto.offset.resetlatestssl.truststore.location$[Path to Trust store]ssl.truststore.password$[Trust store Password]ssl.keystore.location$[Key store location]ssl.keystore.password$[Key store password]ssl.key.password$[ Key password]security.protocolSASL_SSLsasl.mechanismPLAINsasl.kerberos.service.name${KERBEROS_KAFKA_SERVICE_NAME}sasl.jaas.config${SASL_JAAS_CONFIG} -
Click OK.
Next steps
Metadata injection support
All fields of this step support metadata injection. You can use this step with ETL metadata injection to pass metadata to your transformation at runtime.
