Calculator
The Calculator step provides you with predefined functions that you can execute on input field values. This Calculator step is an easy and quick alternative to custom JavaScript commonly used for calculations.
To use, specify the input fields and type of function to perform and return results. You can also specify a field to remove from the result (output) after all values are calculated, which is useful for removing temporary values.
General
Enter the following information in the transformation step field:
- Step name: Specify the unique name of the Calculator step on the canvas. You can customize the name or leave it as the default.
Options
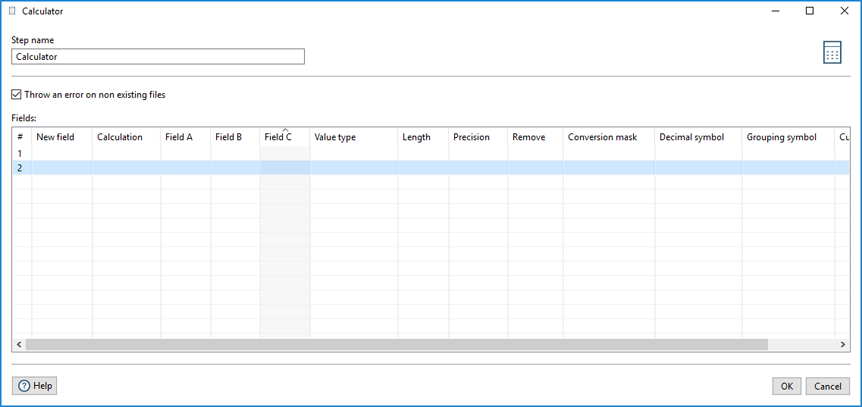
Fill in the following fields in the table. Entries in Field A, Field B, and/or Field C are used by the selected calculator function in the Calculation field.
| Column | Description |
| New field | Specify the name of the field. |
| Calculation | When you click or press in this field, the Select the calculation type dialog box appears. Enter the calculator function to use in the transformation. A description of each function is in the Calculator Functions List. Use the Filter field to search for a specific function. |
| Field A, Field B, and Field C | Enter the value(s) for executing the specified calculator function in the Calculation field. |
| Value type | Select the field's data type from the dropdown list or enter it manually. |
| Length |
Specify the length of the field, according to the following field types:
|
| Precision | Specify the number of floating point digits for number-type fields. |
| Remove | Remove this field from the result (output) after all values are calculated. This field is useful for removing temporary values. Select N or Y. |
| Conversion mask | Specify a format for the field, such as a date format. See Common Formats for information on common valid date formats you can use in this step. |
| Decimal symbol | Specify the symbol used to represent a decimal point, either a dot (.) or a comma (,). For example, 5,000.00 or 5.000,00. |
| Grouping symbol | Specify the method used to separate units of thousands in numbers of four digits or larger, either a dot (.) or a comma (,). For example, 5,000 or 5.000. |
| Currency symbol | Specify the symbol used to represent currencies, for example, $ or €. |
The Calculator step also allows you to indicate if you want errors displayed for the following condition:
- Select the Throw an error on non existing files check box if you want the transformation to generate an error when there are no files to process.
Calculator functions list
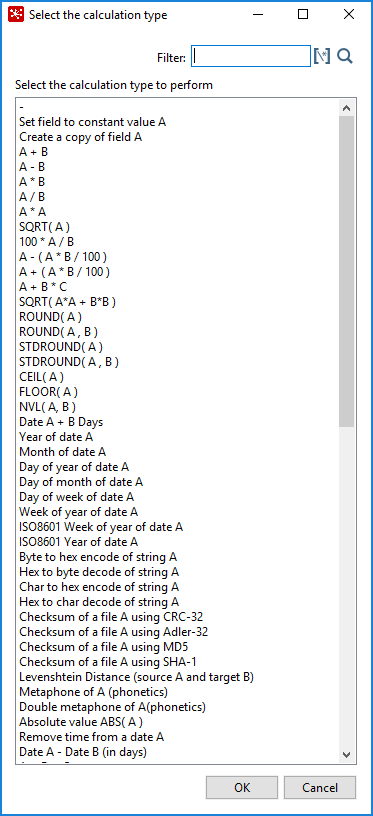
| Function | Description | Required fields |
| Set field to constant value A | Creates a field with a constant value. | A |
| Create a copy of field A | Creates a copy of a field with the given field value. | A |
| A + B | A plus B. | A and B |
| A - B | A minus B. | A and B |
| A * B | A multiplied by B. | A and B |
| A / B | A divided by B. | A and B |
| A * A | The square of A. | A |
| SQRT( A ) | The square root of A. | A |
| 100 * A / B | The percentage of A in B. | A and B |
| A - ( A * B / 100 ) | Subtracts B % of A. | A and B |
| A + ( A * B / 100 ) | Adds B % to A. | A and B |
| A + B *C | Adds A and B times C. | A, B, and C |
| SQRT ( A*A + B*B ) | Calculates (A2 + B2). | A and B |
| ROUND ( A ) | Returns the closest integer to the argument. The result is rounded
to an integer by adding 1/2, taking the floor of the result, and casting the result
to type 'int', such that the result is equal to the value of the expression: floor
(a + 0.5). NoteIf you need the
rounding method "Round half to even", use the following method ROUND( A, B
) with no decimals (B=0). | A |
| ROUND ( A, B ) | Rounds A to the nearest positive infinity number. This rounding
method is known as "Round half to ceiling." NoteThe rounding method prior to
Pentaho 6.0 was the "Round
half to even" method. If you need to use this rounding method, see Rounding method for the Round (A, B)
function in Troubleshooting the Calculator step. | A and B |
| STDROUND( A ) | Rounds A to the nearest integer. The used rounding method is "Round half away from zero." It is also called standard or common rounding, or German mercantile rounding. | A |
| STDROUND( A, B ) | Same rounding method used as in STDROUND (A) but
with B decimals. | A and B |
| CEIL( A ) | The ceiling function maps a number to the smallest following integer. | A |
| FLOOR( A ) | The floor function maps a number to the largest previous integer. | A |
| NVL( A, B ) | If A is not NULL, returns A, else B. Note that sometimes your variable will not be null, but an empty string. | A and B |
| Date A + B Days | Adds B days to Date field A. NoteOnly integer values for B are
supported. If you need non-integer calculations, please add a second calculation
with hours. | A and B |
| Year of date A | Calculates the year of date A. | A |
| Month of date A | Calculates the month of date A. | A |
| Day of year of date A | Calculates the day of year (1-365). | A |
| Day of month of date A | Calculates the day of month (1-31). | A |
| Day of week of date A | Calculates the day of the week (1-7). | A |
| Week of year of date A | Calculates the week of year (1-54). | A |
| ISO8601 Week of year of date A | Calculates the week of the year ISO8601 style. | A |
| ISO8601 Year of date A | Calculates the year ISO8601 style. | A |
| Byte to hex encode of string A | Encodes bytes in a string to a hexadecimal representation. | A |
| Hex to byte decode of string A | Decodes bytes in a string from its hexadecimal representation (add a leading 0 when A is of odd length). | A |
| Char to hex encode of string A | Encodes characters in a string to a hexadecimal representation. | A |
| Hex to char decode of string A | Decodes a string from its hexadecimal representation (add a leading 0 when A is of odd length). | A |
| Checksum of a file A using CRC-32 | Calculates the checksum of a file using CRC-32. NoteThis function is ignored by Spark
when you run the PDI
transformation on the Spark engine. | A |
| Checksum of a file A using Adler-32 | Calculates the checksum of a file using Adler-32. NoteThis function is ignored by Spark
when you run the PDI
transformation on the Spark engine. | A |
| Checksum of a file A using MD5 | Calculates the checksum of a file using MD5. NoteThis function is ignored by Spark
when you run the PDI
transformation on the Spark engine. | A |
| Checksum of a file A using SHA-1 | Calculates the checksum of a file using SHA-1. NoteThis function is ignored by Spark
when you run the PDI
transformation on the Spark engine. | A |
| Levenshtein Distance (source A and target B) | Calculates the Levenshtein Distance. | A and B |
| Metaphone of A (phonetics) | Calculates the Metaphone of A. | A |
| Double metaphone of A (phonetics) | Calculates the Double Metaphone of A. | A |
| Absolute value ABS ( A ) | Calculates the absolute value of A. | A |
| Remove time from a date A | Removes time value of A. NoteDaylight Savings Time (DST) changes
in Sao Paulo and some other parts of Brazil at midnight 0:00. This practice makes
it impossible to set the time to 0:00 at the specific date, when the DST changes
from 0:00 to 1:00 am. So there is one date in one year in these regions where this
function will fail with an "IllegalArgumentException: HOUR_OF_DAY: 0 -> 1"
error. This issue does not occur in Europe, the US, and other regions where the
time changes at 1:00 or 2:00 or 3:00 am. | A |
| Date A - Date B (in days) | Calculates difference, in days, between A date field and B date field. | A and B |
| A + B + C | A plus B plus C. | A, B, and C |
| First letter of each word of a string A in capital | Transforms the first letter of each word within a string. | A |
| UpperCase of a string A | Transforms a string to uppercase. | A |
| LowerCase of a string A | Transforms a string to lowercase. | A |
| Mask XML content from string A | Escapes XML content; replaces characters with '& values'. | A |
| Protect (CDATA) XML content from string A | Indicates an XML string is general character data, rather than
non-character data or character data with a more specific, limited structure. The
given string will be enclosed into
<![CDATA[String]]>. | A |
| Remove CR from a string A | Removes carriage returns from a string. | A |
| Remove LF from a string A | Removes linefeeds from a string. | A |
| Remove CRLF from a string A | Removes carriage returns/linefeeds from a string. | A |
| Remove TAB from a string A | Removes tab characters from a string. | A |
| Return only digits from string A | Outputs only digits (0-9) from a string from a string. | A |
| Remove digits from string A | Removes all digits (0-9) from a string. | A |
| Return the length of a string A | Returns the length of the string. | A |
| Load file content in binary | Loads the content of the given file (in field A) to a binary data
type (e.g. pictures). NoteThis
function is ignored by Spark when you run the PDI transformation on the Spark
engine. | A |
| Add time B to date A | Add the time to a date, returns date and time as one value. | A and B |
| Quarter of date A | Returns the quarter (1 to 4) of the date. | A |
| variable substitution in string A | Substitutes variables within a string. | A |
| Unescape XML content | Unescapes XML content from the string. | A |
| Escape HTML content | Escapes HTML within the string. | A |
| Unescape HTML content | Unescapes HTML within the string. | A |
| Escape SQL content | Escapes the characters in a String to be suitable to pass to an SQL query. | A |
| Date A - Date B (working days) | Calculates the difference between Date field A and Date field B (only working days Mon-Fri). | A and B |
| Date A + B Months | Add B months to Date field A. NoteOnly integer values for B are
supported. If you need non-integer calculations, please add a second calculation
with days. | A and B |
| Check if an XML file A is well formed | Validates XML file input. NoteThis function is ignored by Spark
when you run the PDI
transformation on the Spark engine. | A |
| Check if an XML string A is well formed | Validates XML string input. | A |
| Get encoding of file A | Provides a guess of the best encoding (UTF-8) for the given
file. NoteThis function is ignored
by Spark when you run the PDI transformation on the Spark engine. | A |
| DamerauLevenshtein distance between String A and String B | Calculates the Damerau-Levenshtein distance between strings. | A and B |
| NeedlemanWunsch distance between String A and String B | Calculates the Needleman-Wunsch distance between strings. | A and B |
| Jaro similitude between String A and String B | Calculates the Jaro similarity coefficient between two strings. | A and B |
| JaroWinkler similitude between String A and String B | Calculates the Jaro-Winkler distance between two strings. | A and B |
| SoundEx of String A | Encodes a string into a Soundex value. | A |
| RefinedSoundEx of String A | Retrieves the Refined Soundex code for a given string object | A |
| Date A + B Hours | Adds B hours to Date field. NoteOnly integer values for B are
supported. If you need non-integer calculations, please add a second calculation
with minutes. | A and B |
| Date A + B Minutes | Adds B minutes to Date field. NoteOnly integer values for B are
supported. If you need non-integer calculations, please add a second calculation
with seconds. | A and B |
| Date A - Date B (milliseconds) | Subtracts B milliseconds from Date field A | A and B |
| Date A - Date B (seconds) | Subtracts B seconds from Date field A. NoteOnly integer values for B are
supported. If you need non-integer calculations, please add a second calculation
with milliseconds. | A and B |
| Date A - Date B (minutes) | Subtracts B minutes from Date field A. NoteOnly integer values for B are
supported. If you need non-integer calculations, please add a second calculation
with seconds. | A and B |
| Date A - Date B (hours) | Subtracts B hours from Date field A. NoteOnly integer values for B are
supported. If you need non-integer calculations, please add a second calculation
with minutes. | A and B |
| Hour of Day of Date A | Extracts the hour part of the given date. | A |
| Minute of Hour of Date A | Extracts the minute part of the given date. | A |
| Second of Minute of Date A | Extracts the second part of a given date. | A |
| ROUND_CUSTOM( A , B ) | Rounds A using a specific type of rounding mode indicated by B . B
must be a number, and can be an integer or decimal value. If B is a decimal value,
then it will convert to the floor value, such that '5.7' = 5 and '1.1' = 1.
Rounding Modes:
| A and B |
| ROUND_CUSTOM( A , B , C ) | Rounds B using a specific type of rounding mode indicated by C.
Calculates using the same conditions as the ROUND_CUSTOM( A , B ) function with the
following exceptions:
| A, B, and C |
| Date A + B Seconds | Adds the number of milliseconds offset from the Epoch of A to the same of B, where A and B are dates. | A and B |
| Remainder of A / B | Returns the remainder of dividing B into A. This remainder can be an integer or decimal value. For example, if A is '100' and B is '56', then the remainder is 44. If A is '2.5' and B is '2.3', then the remainder is 0.2. | A and B |
Troubleshooting the Calculator step
The following are frequently asked questions about the Calculator step.
Length and precision
Question
I made a transformation using the A/B function and it rounded incorrectly. I entered integers in Field A and Field B, but my result type was a number, so I would expect the integers to be converted to numbers before executing the division.
For example, when I execute 28/222, the result is 0.0 instead of 0.1261 which is expected behavior. It seems the result type is ignored. If I change the values in Field A and Field B to numbers (6, 4) my result is 0.12612612612612611 which still ignores the result type (4 places after the comma).
Suggested Solution
Length and Precision are metadata pieces. We convert to the required metadata type when we result the data to a location, not during the transformation.
If you want to round to the specified precision, you should do this rounding in another step. However, rounding double point precision values is futile anyway. A floating point number is stored as an approximation, so 0.1261, your desired output, would probably be stored as 0.126099999999 or 0.1261000000001.
NoteThis behavior is not true for the data type BigNumbers.So the calculation is rounded using BigDecimals once the numbers are stored in the output table, but not during the transformation.
NoteThis behavior is also true for the Text File Output step. If you would have specified Integer as the result type, the internal number format would have been retained. When you press Get Fields, the required Integer type would be filled in. Then the required conversion would occur at this point. See Using the Text File Output step on the Pentaho engine for details.
Data Types
Question
How do the data types work internally?
Suggested Solution
You might notice that if you multiply an integer and a number, the result is always rounded. The Calculator step uses the data type of the value to the left side of the multiplication calculation, in this case the value in Field A, as the driver for the calculation.
If you want more precision, place the value in Field B on the left side of the calculation. Alternatively, change the data type of Field A to Number.
Rounding method for the Round (A, B) function
Procedure
Open the
kettle.propertiesfile in a text editor. By default, thekettle.propertiesfile is typically stored in your home directory or the.pentahodirectory.Edit the file and add the following lines:
ROUND_2_MODE=ROUND_HALF_EVEN ROUND_2_MODE_BACKWARD_COMPATIBILITY_VALUE=ROUND_HALF_EVEN
When complete, close and save the file.

