Execute SQL Script
You can execute SQL scripts with this step using either of the following methods:
- Execute the SQL script once, during the initialization phase of the transformation.
- Execute the SQL script once for every input row that is sent to this step.
Notes
- Prepared SQL statements are not used due to the scripting and dynamic operation of this step, which can adversely affect transformation performance. If optimal performance is desired, then Pentaho recommends using dedicated steps like Table Output, Table Input, Update, or Delete.
- If the transformation halts unexpectedly, verify whether the Execute for each row? option is selected. For the SQL to start at the initialization phase of the transformation, ensure that Execute for each row? is not selected.
General
The following fields are general to this transformation step:
| Field | Description |
| Step name | Specify the unique name of the Execute SQL Script step on the canvas. You can customize the name or leave it as the default. |
| Connection | Select the name of a connected database from the list. |
| Edit (button) | Click to edit your current database connection. |
| New (button) | Click to establish a new database connection. |
| Wizard (button) | Click to open a new database connection using the database explorer. |
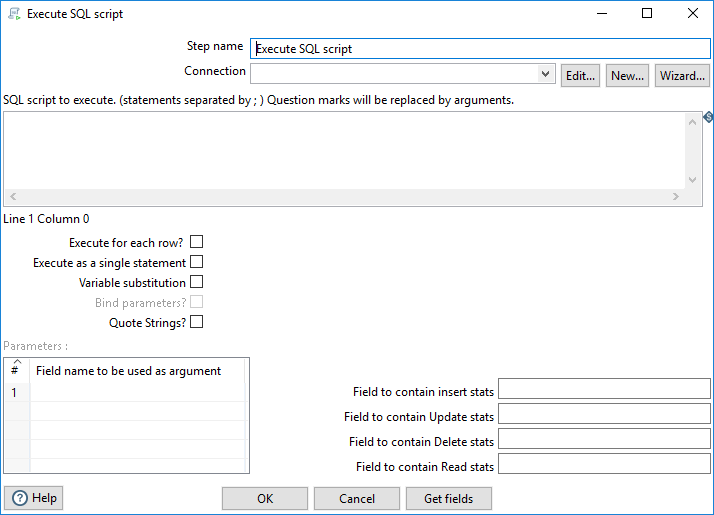
Options
The Execute SQL Script step has the following options:
| Option | Description |
| SQL script to execute |
Enter the SQL to execute. Separate statements with a semi-colon ( ; ) and use question marks as placeholders for parameters. The given parameters must be enclosed correctly. Numeric values do not need to be enclosed, but all others (for example, strings) must be enclosed with single quotation marks ( ' ) or double quotation marks ( " ) depending on the database dialect. The Bind parameters? and Quote Strings? options (explained below) are also allowed. |
| Execute for each row? |
|
| Execute as a single statement |
Select this option to send the entire SQL statement to the database. Leave this option unselected to split the statement semi-colons ( ; ). |
| Variable substitution | Select this option to include the use of variables in the SQL (for example: ${table_name} ). |
| Bind parameters? |
Select this option to bind parameters using prepared statements. Leave this option unselected if you want this step to perform a string replacement of the parameters. NoteTo use this option, the Execute for each row? option must also be selected.
|
| Quote Strings? |
Select this option to add quotation marks ( " ) around the string
according to the database dialect and escape special characters like
NoteTo use this option, the Execute for each row? option must also be selected.
|
| Parameters |
There are two ways to populate the parameters:
Using a Select Values step, you can duplicate field values within the Select & Alter tab by selecting the value once and renaming it a second or third time. To use this option, the Execute for each row? option must also be selected. |
| Get Fields (button) | Click to automatically populate the parameters in the Execute SQL Script with the same parameters that are specified in the transformation step previous to Execute SQL Script. |
Optional statistic fields
Use these optional fields to collect statistics when the Execute for each row? parameter is selected. Each option will create a field in the data stream that contains the specific type of statistic.
| Field | Description |
| Field to contain insert stats | Specify a field name to contain the statistic for the number of records that were inserted. |
| Field to contain Update stats | Specify a field name contain the statistic for the number of records that were updated. |
| Field to contain Delete stats | Specify a field name to contain the statistic for the number of records that were deleted. |
| Field to contain Read stats | Specify a field name to contain the statistic for the number of records that were read. |
Example
If you want to create five tables (tab1, tab2, tab3, tab4, and tab5), you could create a transformation similar to this one:
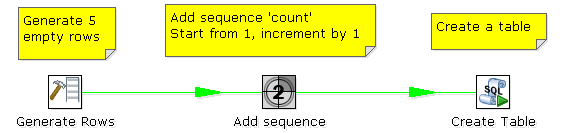
The SQL script to execute might look like this:
CREATE TABLE tab? ( a INTEGER );
The field name to specify as the parameter is then the "count" sequence defined in the second step.
As an extra option, you can return the total number of inserts (INSERT INTO statements), updates (UPDATE table), deletes (DELETE FROM table) and reads (SELECT statements) by specifying the field names in the lower right of the dialog box.
Metadata injection support
All fields of this step support metadata injection. You can use this step with ETL metadata injection to pass metadata to your transformation at runtime.
